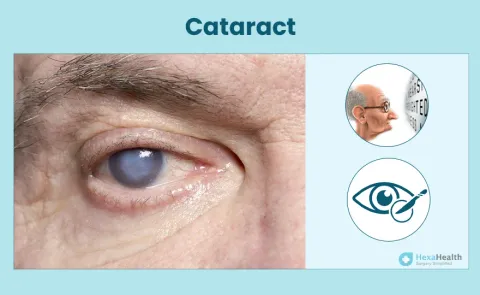
Myth: Cataract only affect the elderly.
Fact: While cataract are most common in older adults, they can occur at any age. Certain factors like genetics or previous eye injuries can also contribute to the development of cataract in younger individuals.
Myth: Cataract can be cured with eye drops or medication.
Fact: Eye drops and medications cannot reverse or cure cataract. The only effective treatment for cataract is surgery to replace the cloudy lens with an artificial one.
Myth: Cataract surgery is risky and painful.
Fact: Cataract surgery is a safe and commonly performed procedure. It is typically done on an outpatient basis and is considered to be one of the safest surgeries in medicine. Most patients experience minimal discomfort during and after the procedure, with a quick recovery time.
Myth: Wearing glasses can prevent or slow down the progression of cataract.
Fact: While wearing glasses can help improve vision and manage symptoms associated with cataract, they cannot prevent or slow down the condition's progression. Surgery is the only effective treatment for cataract.
Myth: Cataract always lead to blindness.
Fact: Cataract can cause vision impairment, but they do not always result in complete blindness. With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, vision can be restored and cataract-related visual impairments can be significantly improved. It is important to address cataract early to prevent them from negatively impacting daily activities and quality of life.